- +91 8368910203
- anamikaabhi1103@gmail.com
- CK Birla Hospital, Gurgaon | Sync Orthopaedic and Pain Management
Radiofrequency Ablation
A minimally invasive medical technique called radiofrequency ablation (RFA) uses heat produced by radiofrequency radiation to kill aberrant tissue. It is frequently used to treat a number of ailments, such as cancer, persistent pain, and specific heart arrhythmias. An outline of the process’s applications, advantages, and dangers is provided below:
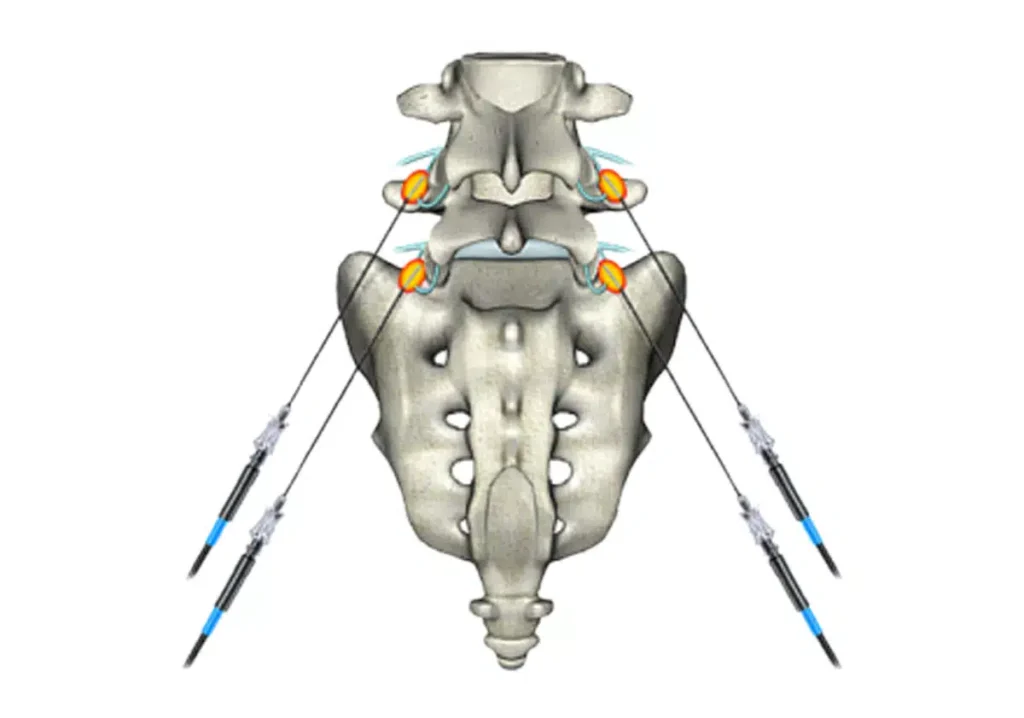
Mechanism of Radiofrequency Ablation :
- RFA involves inserting a thin, flexible tube called a catheter into the body, typically guided by imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT, or fluoroscopy.
- Once the catheter is in place, radiofrequency energy is delivered through the catheter to heat and destroy the targeted tissue.
Common Uses of RFA
- Tumor Treatment: When surgery is not an option, RFA is frequently used to treat tumors in organs such the liver, kidneys, lungs, and bones.
- Chronic Pain Management: By focusing on nerve tissue, it can be utilized to treat chronic pain disorders, especially those affecting the joints or spine.
- Cardiac Arrhythmias: By ablating the tiny regions of cardiac tissue that produce the erratic beats, RFA is used in cardiology to treat abnormal heart rhythms, or arrhythmias.
- Varicose Veins: By heating and rupturing the vein wall, RFA can be used to seal off varicose veins.
Benefits of RFA
- Minimally Invasive: Usually done as an outpatient procedure with tiny incisions, this procedure requires less recovery time than standard surgery.
• Less discomfort and Scarring: Less trauma to the surrounding tissues results in fewer scars and less discomfort.
• Fast Recovery: Compared to surgical treatments, patients frequently resume their regular activities sooner.
• Effective Treatment: RFA can be very helpful in treating some cancers and illnesses, reducing symptoms and enhancing quality of life.